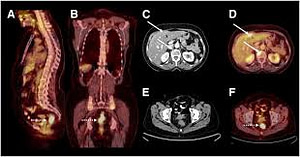
What is a PET/CT SCAN
Positron emission tomography (PET), also called PET imaging or a PET scan, is a type of nuclear medical imaging that produce 3 dimension images of biological functions. PET scans can not only diagnose health conditions, but are helpful in determining how a condition is developing.
Nuclear medicine imaging procedures are primarily noninvasive and usually painless medical tests that use radioactive materials called radiotracers. Radiotracers are designed to bond with certain chemicals within the body, like glucose, and highlight areas that are using those chemicals.
PET scans are often combined with X-rays, MRIs or CT scans to produce a more complete picture that can pinpoint disease centers in the body. Combining multiple types of imaging gives physicians more precise information and leads to more accurate diagnoses of cancer, heart disease and brain disorders.
Benefits of a PET/CT Scan
- PET/CT provides a very accessible and comfortable, patient friendly imaging device
- PET/CT combines the superior anatomical imaging of CT with the excellent biochemical functioning capturing of PET to provide superior lesion and tumor localization from near perfect analytical and functional imaging.
- PET/CT provides greater distinction between physiological (organ) uptake and pathological (cancerous) uptake of tracer, allowing better diagnosis of cancerous masses.
- PET/CT is more time efficient as the CT and PET scans can be completed in 30-45minutes, where as a PET scan alone can take up to 60 minutes. Also time is saved carrying out the PET and CT scans at the same time, than on separate machines. This is important for quick detection and treatment planning.
- PET/CT detects 80% of tumors, as opposed to MRI, which only detects 52% of all tumors. PET/CT is also 33% more likely to accurately detect a tumor that separate CT and PET scans that are used together.
- PET/CT allows both PET and CT scans to be performed simultaneously with a constant geometry and patient positioning, removing problems with internal organ and patient movement that affected separate CT and PET scans used together.
- PET/CT can help avoid un-necessary procedures such as invasive surgery to see if a tumour exists.
- PET/CT combines to give a more accurate picture of the internal workings of the body
- PET/CT can detect tumours as small as 4mm in total length
- PET/CT can help assist surgeons in planning a form of treatment or route to the target tumour, because it offers a more complete picture as there is more detail as well as both functional and anatomical information on the same image
- PET/CT can help detect cancer earlier, even before symptoms arise
- PET/CT provides excellent patient monitoring options, both in seeing if all cancer has been removed or if cancer has reoccurred.
- PET/CT can help surgeons decide if surgery is an option
- PET/CT can help determine if someone is at risk of coronary illness, before symptoms occur
- PET/CT is beneficial in helping diagnose mental illnesses earlier, helping treat the problem before it develops.
- PET/CT files can be imported into radiation therapy planning computers, aiding surgery.
- PET/CT can help to determine earlier if a cancer treatment is working or not.
Risks of a PET/CT Scan
The PET scan involves radioactive tracers, but the exposure to harmful radiation is minimal. The risks of the test are minimal compared with how beneficial the results can be in diagnosing serious medical conditions. The tracer is essentially glucose (sugar) with the radioactive component attached. This makes it very easy for your body to eliminate the tracers, even if you have a history of kidney disease or diabetes.
Result
All of our diagnostic examinations are interpreted by Board-Certified Radiologists and Nuclear Medicine Specialists. The results of your PET/CT scan will be sent to your referring physician as soon as they are interpreted. It is the patients´ responsibility to contact their referring physician to discuss the results of their examination and ask for further recommendations
Preparation
– Please follow a low carbohydrate diet for 24 hours.
– Make sure you are on time for your exam.
– Wear comfortable clothing.
– Plan to spend two hours at the facility, exams times and procedures vary with each patient.